The Ultimate Guide to ESD Shielding for Membrane Switches
Understanding the Importance of ESD Shielding
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) is a critical concern in electronic device design, particularly for sensitive components like membrane switches. Without proper ESD protection, these switches can suffer from performance issues, reduced lifespan, or even total failure. Here’s why ESD shielding is essential:
Why is ESD Shielding Necessary for Membrane Switches?
Membrane switches are often used in medical devices, industrial control panels, military equipment, and consumer electronics—all environments where electrostatic discharge is common. Since membrane switches are made from thin polymer layers and conductive traces, they are highly susceptible to ESD damage, which can cause malfunctions or render them inoperable.
What Happens if a Membrane Switch Isn’t Protected Against ESD?
Without ESD shielding, static discharge can lead to:
- Erratic Functionality – Unintended triggering or failure of key presses.
- Damage to Circuitry – Permanent breakdown of conductive traces and electronic components.
- Shortened Lifespan – Increased wear and tear due to repeated exposure to electrostatic events.
- Safety Risks – In applications such as medical or aerospace, switch failures due to ESD can have severe consequences.
How Does ESD Affect the Lifespan and Reliability of a Membrane Switch?
A well-designed membrane switch with proper ESD shielding ensures:
- Consistent Performance – Eliminating false triggers and response delays.
- Longer Operational Life – Preventing early degradation of conductive pathways.
- Improved Durability – Resistance to environmental factors like humidity and static buildup.
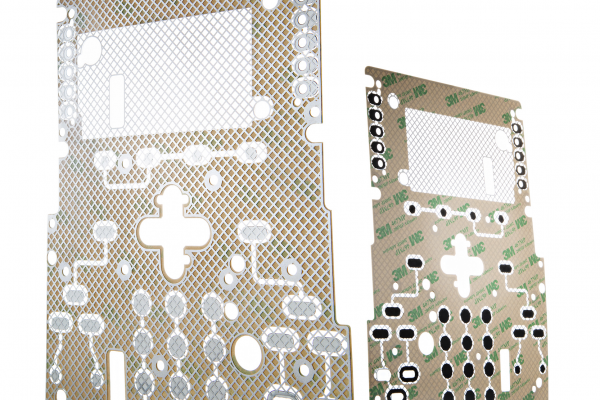
Materials & Construction of ESD Shielding
To protect membrane switches from ESD, various materials and techniques are used to distribute and dissipate static charges safely.
What Materials Are Used for ESD Shielding in Membrane Switches?
Common materials include:
- Carbon-based conductive coatings
- Silver conductive ink layers
- Metalized shielding layers (aluminum or copper)
- Transparent conductive films (ITO – Indium Tin Oxide)
How Does a Carbon or Silver-Based Conductive Layer Work in Shielding?
- Carbon-based layers provide cost-effective ESD protection by forming a conductive path that redirects electrostatic charges away from sensitive components.
- Silver-based conductive inks offer higher conductivity than carbon and are ideal for applications requiring superior performance and durability.
What is the Role of Metalized Shielding Layers?
- Aluminum or copper shielding creates a Faraday cage effect, preventing ESD from penetrating and reaching internal circuitry.
- These layers are often laminated within the membrane switch for maximum protection.
Can Transparent Conductive Films Be Used for ESD Shielding?
Yes. Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) films provide ESD protection while maintaining transparency, making them ideal for membrane switches that incorporate touchscreens or backlit displays.
Design & Implementation of ESD Shielding
Proper design considerations are crucial to effectively integrate ESD shielding into membrane switches without compromising usability.
How Do You Incorporate ESD Shielding into a Membrane Switch Design?
- Layer Integration – Shielding layers are added within the membrane switch stack-up.
- Strategic Routing – Conductive traces are carefully designed to direct static charges away.
- Grounding Integration – ESD shielding must be properly grounded to function effectively.
What Are the Different Grounding Methods for ESD Protection?
- Direct Grounding – Connecting shielding layers directly to the device’s chassis or ground plane.
- Floating Shielding – Using isolated shielding layers for controlled dissipation.
- Resistive Grounding – Implementing a resistor to control the rate of static discharge.
Should ESD Shielding Be Connected to a Ground Plane or Chassis?
Yes. Direct grounding to a chassis or PCB ground plane is the most effective way to ensure that static charges are safely dissipated, reducing the risk of ESD-related failures.
How Does Shielding Affect the Tactile Feel and Thickness of the Switch?
- Minimal Impact – Modern shielding materials are ultra-thin and flexible, maintaining switch responsiveness.
- Enhanced Durability – Additional layers may slightly increase thickness but significantly improve reliability.
- Customizable Design – Engineers can balance shielding and switch feel based on application needs.
Final Thoughts
Integrating ESD shielding into membrane switch design is a proactive approach to ensuring longevity, reliability, and safety. Whether through carbon coatings, silver inks, metalized layers, or transparent conductive films, choosing the right shielding method depends on application-specific requirements. Proper grounding and thoughtful implementation will help manufacturers produce durable, high-performance membrane switches resistant to ESD threats.
More from Ken
In today’s rapidly evolving technological environment, the need for innovative and dependable membrane switch prototypes is continuously increasing. As a leading membrane switch manufacturer, JN White excels in crafting custom membrane switch prototypes that not only meet your specific design…
Projected Capacitive (PCAP) touch technology has revolutionized modern touchscreens, providing highly responsive, durable, and intuitive user experiences. From smartphones to industrial control panels, PCAP touchscreens are now the gold standard for applications requiring precision and reliability. At JN White, we…
In an age where electronic devices are at the core of nearly every industry, protecting sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) is crucial. One of the most effective solutions for shielding electronics from these disruptive…